With the continuing need to drive greater throughput and reduce costs, manufacturers are turning to automating systems and Industry 4.0 solutions to increase their efficiency. Within this article, we will be exploring the use of automation in manufacturing, including the different types of automation, examples of automated manufacturing, and the primary benefits of automation.
What is Manufacturing Automation?
Automation, in the context of manufacturing, is the use of equipment to automate systems or production processes. The end goal is to drive greater efficiency by either increasing production capacity or reducing costs, often both.
Automation has become known more as using machines to reduce work performed by humans. It has become associated with electromechanical systems that are programmed to perform many types of processes. While automation may not be right for every manufacturer, most companies are able to find benefits in one of the following types of automation: Fixed, programmed, or flexible.
Types of Manufacturing Automation
Fixed Automation
Characterized by large volume production and a high barrier of entry, fixed automation often has a set task. Also called hard automating, most programming is contained within individual machines. The speed and sequence of processes are set by the equipment or production line.
An example of fixed automation can be found in the body-in-white and automotive panels. Major vehicle suppliers might produce over a million parts before changing designs. Additionally, processes such as stamping or casting are used which may not require control systems as sophisticated as automated milling or robotic welding.
Often the production volume associated with fixed automation does not have time for changeovers. However, if any changes are made to fixed automation it would likely require a line to be shut down and for technicians to manually swap tooling. The expense and time associated with this downtime are high. For low volume or products that have shorter life cycles consider programmable automation.
Programmable Automating
Characterized by making several dozens to thousands of units, programmable automation is associated with batch production. Programmable automation offers the ability to produce more types of parts or products. However, downtime is needed to perform changeovers. This downtime is expected and taken into consideration for batch sizes and lead times. However, downtime is expensive and has led to an extension of programmable automation called flexible automation.
Flexible Automation
Flexible automation is able to perform changeovers automatically. This may limit equipment to run parts that share similar tools or require additional devices to make automated changeovers possible.
Additionally, since programs need to be changed, flexible automation is often connected to some form of network that increases value by offering remote monitoring or control. Programs are developed offline on a computer. Depending on how the device is connected, a designer could upload, run new programs, or work them into existing production from anywhere in the world.
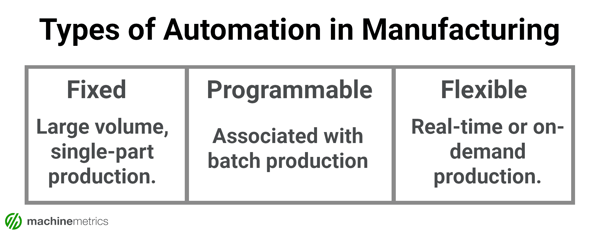
Examples of Manufacturing Automation
To remember the different types of automation consider the following examples:
- Fixed Automation: Associated with large volume, single-part production. EX: A hobbing machine dedicated to automatically producing one gear.
- Programmable Automation: Associated with batch production. EX: A hobbing machine that automatically produces different types of gears, but a changeover will cause downtime to change gears.
- Flexible Automation: Associated with real-time or on-demand production. EX: A hobbing machine that automatically produces several gears without the need to be shut down or manual changeovers.
Automation in manufacturing is growing and continues to shape the factory floor. Manufacturers are striving for a full digital thread from tracking materials supply chains, to production, to delivery. However, before a full digital transformation, it is important to know your goals, and how they align with the benefits of automated manufacturing strategies.
Benefits of Automating in Manufacturing
Manufacturers are increasingly using automation to drive precision, consistency, and greater operational efficiency. To start, know your goals. The more specific the goals, the easier it is to align with a solution. Goals such as increasing production, while general, indicate that you must know what affects production. Easy and quick to integrate sensors and devices that monitor equipment and produce user-friendly data, graphics, etc. will help connect production lines and serve other benefits:
- Reduce downtime
- Provide predictable maintenance
- Improve decision making
Having devices to monitor materials in inventory or at a workstation can reduce downtime due to running out of stock. Being able to see equipment run times might be enough to reduce downtime by adjusting workflow to reduce changeovers, or indicate where an investment in more automation would yield a positive ROI.
Monitoring can also track equipment performance to indicate when maintenance or failures might occur. Performance tracking can help make smarter operation decisions and schedule maintenance when it will least affect production. Also, automation and monitoring drive more informed business decisions.
Having real-time data can help manufacturers understand lead times and provide more accurate estimates and timelines. Additionally, automated devices improve repeatability that can improve quality and reduce variability in production. Overall, automated monitoring offers a more predictable model to make business decisions from, while providing transparency for all stakeholders.
The future of automation in manufacturing is progressing with robotics, machine vision, IIoT, and other digital technologies. To take advantage of the growth in automation, know your goals, what affects production, and what benefits each technology provides. When in doubt, minimize complexity, follow proper engineering principles, and work with vendors that provide good customer service.
Getting Started with Automation
How can you get started with automating processes within your operation? The first step is by connecting your machines so that you have the ability to collect data, process it, and make decisions. Only then will you have the insight into operational performance across both your equipment and staff to automate processes and drive greater efficiency across the shop floor.
Article Provided By: Machine Metrics

TSVMap is here to help grow manufacturing processes and consult your IT Solutions that way we can make it more effective and efficient. So if you need: IT Solutions, Consultants, ERP Systems, MRP Systems, Automations, or Cyber Security. Contact us today at 864-991-5656 or Email info@tsvmap.com







0 Comments